The White Flight From Football
Parents know that football comes with a risk of brain damage. But many black families feel that the sport is still the best option for their kids.
Updated at 5:41 p.m. ET on February 1, 2019.
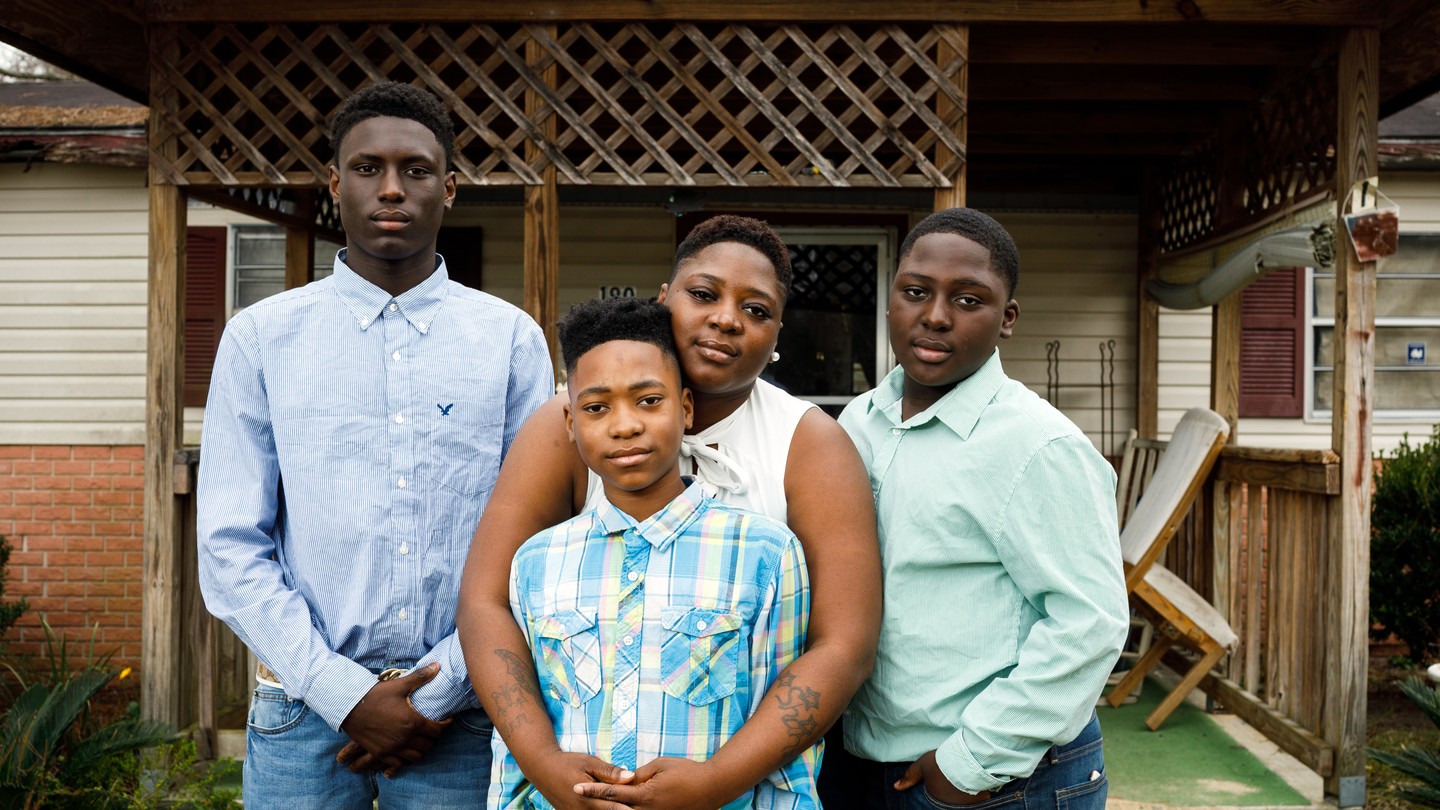
Shantavia Jackson signed her three sons up for football to keep them out of trouble. As a single mother who works the night shift at a Home Depot warehouse 50 minutes away from her house, Jackson relies on the sport to shield the boys from gang activity in her rural Georgia county. They began in a local league five years ago when they were still little, their helmets like bobbleheads on their shoulders. Now 11, 12, and 14, they play in games across the region. Jackson says she passed up a daytime shift at Home Depot so that she can drive them to games and cheer them on.
Over time, the boys’ coaches have become mentors, making sure their athletes get good grades and stay off the streets. They take the boys on field trips to the beach and to Busch Gardens. Jackson’s eldest son, Marqwayvian McCoy—or Qway, as she calls him—has particularly thrived. Jackson says Qway has been diagnosed with schizoaffective bipolar disorder, which sometimes manifests in bursts of anger and an inability to focus at school. Now his teammates help him when he gets stuck in his studies and look up to him for his prowess on the field. They’ve nicknamed him Live Wire because he can hit so hard.
Jackson dreams that Qway will soon make it out of their home in Colquitt County, a place marked by fields of crops and cotton bales the size of Mack trucks. Football could help him do that. As a middle schooler, he’s already been asked to practice with the high-school team, the Colquitt County Packers, a national powerhouse that in 2016 sent two dozen boys to college with full scholarships. Qway knows his mother doesn’t have the money to send him to college, so he studies websites that track top high-school-football athletes and watches all the football he can online, hoping to get better at the game.
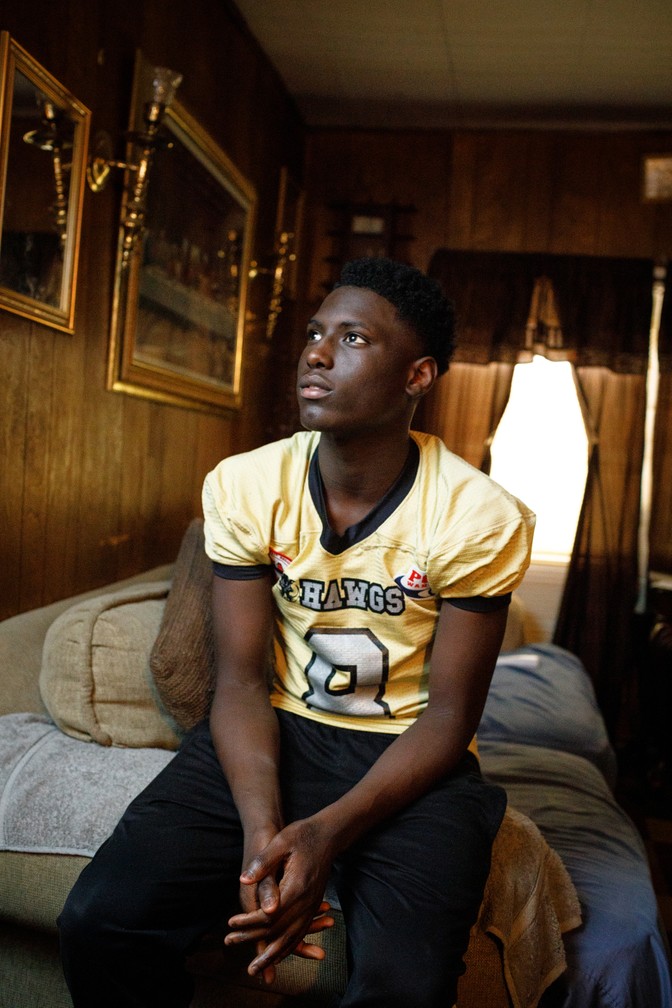

As Qway throws himself into football, the sport is facing a highly publicized reckoning more serious than any it has confronted since the Pop Warner youth-football program was established in 1929. Research suggests that tackle football can cause long-term brain injury, and as a result, many parents are telling their kids they can’t play. In the 2017–18 school year, 6.6 percent fewer high-school athletes participated in 11-player tackle football than in the 2008–09 school year, according to the National Federation of State High School Associations.
Yet not all parents are holding back their kids from tackle football at equal rates, which is creating a troubling racial divide. Kids in mostly white upper-income communities in the Northeast, Midwest, and West are leaving football for other sports such as lacrosse or baseball. But black kids in lower-income communities without a lot of other sports available are still flocking to football. In keeping with America’s general racial demographics, white boys continue to make up the majority of youth-tackle-football players, according to data from the Sports and Fitness Industry Association. But proportionally, the scales appear to be shifting. A recent survey of 50,000 eighth-, tenth-, and 12th-grade students found that about 44 percent of black boys play tackle football, compared with 29 percent of white boys, as analyzed by the University of Michigan sociologist Philip Veliz. Football at the high-school level is growing in popularity in states with the highest shares of black people, while it’s declining in majority-white states. Other recent studies suggest that more black adults support youth tackle football than white adults.
This trend has become particularly visible as majority-white towns such as Ridgefield, New Jersey, and Healdsburg, California, have dropped their varsity-football programs due to a lack of interest. Meanwhile, in Lee County, Georgia, a majority-black area near where the Jacksons live, a coach recently started a new travel football team for kids to provide them with guidance and mentorship. These racial divides show up in the football that America watches: Today black athletes make up nearly half of all Division I college-football players, up from 39 percent in 2000. White athletes make up 37 percent, down from 51 percent.
This divergence paints a troubling picture of how economic opportunity—or a lack thereof—governs which boys are incentivized to put their body and brain at risk to play. Depending on where families live, and what other options are available to them, they see either a game that is too violent to consider or one that is necessary and important, if risky. Millions of Americans still watch football; NFL ratings were up this season. That a distinct portion of families won’t let their children play creates a disturbing future for the country’s most popular game.
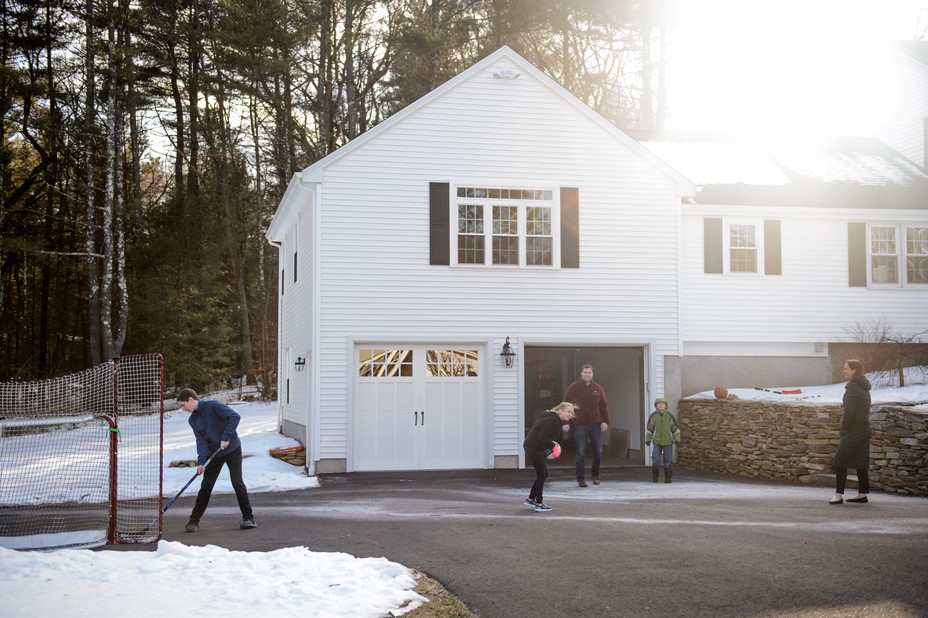
Sam and Megan Taggard’s colonial-style home in West Simsbury, Connecticut, has no shortage of sporting equipment. The couple’s four children stack bikes in the garage and clutter the wooden living-room floor with footballs and tennis balls. On the day I visited them last October, the Taggards’ 13-year-old son had two hockey games and their 9-year-old daughter had a basketball game. The family’s two younger sons horsed around a hockey goal in the living room.
Tackle football, however, was not on the agenda. “My kids aren’t playing,” Sam Taggard told me. Taggard played football years ago at Bentley University, and he says his 44-year-old body is still bearing the damage: He had back surgery two years ago and still feels the wear and tear of football on his body.* He also did a clinical doctorate in physical therapy and has seen how debilitating head and neck injuries can be. Football requires kids to endanger their brain every single game, he said: “In football, you’re literally trying to decimate the person in front of you. If you’re not, you’re not playing well.”

The Taggards aren’t the only family in their neighborhood pulling their boys from tackle football. At one of the day’s hockey games, I chatted with five other parents—all of whom were white—in the frigid stands of an ice-hockey rink on a private-school campus as their sons skated past. Four told me they wouldn’t let their son play. The fifth, a mother named Sharon Walsh, said she had objected, but her husband and son overruled her. She hated signing the waiver saying that she understood her child might die. Thankfully, she said, her son recently decided to give up football on his own.
Ron Perry, another hockey parent, echoed the sentiment that he wouldn’t let his son play tackle football, because of concerns about concussions and head injuries. A friend of his coaches a rec-football team and is always looking for players, Perry told me. But he wouldn’t recommend his son. “There’s just constant hitting,” he said. (Hockey, it should be noted, can also lead to head injuries. USA Hockey, which oversees high-school and club hockey in America, has been relatively proactive about safety, deciding in 2011 to ban bodychecking in games until age 13.)
A huge amount of evidence shows that football poses a risk to developing brains. Athletes who begin playing tackle football before the age of 12 have twice as much of a risk of behavioral problems later in life and three times as much of a risk of clinical depression as athletes who begin playing after 12, according to a 2017 Boston University study. A separate study from Wake Forest University found that boys who played just one season of tackle football between the ages of 8 and 13 had diminished functions in part of their brain.
One of the biggest risks of repeated head injuries is that players could develop CTE, or chronic traumatic encephalopathy, a condition that occurs when a protein called tau spreads through the brain, killing brain cells. CTE is linked with behavioral and personality changes, memory loss, and speech problems. Conversations about CTE tend to focus on the dangers of concussions, but brains can also be damaged by frequent hits to the head. A February 2018 study found that mice with repeated traumatic brain injuries, regardless of concussive symptoms, still had CTE. The condition has been found in the brains of many high-profile football players who committed suicide in recent years, including Junior Seau, Andre Waters, and Terry Long. One 2017 study of the brains of 111 former NFL players found that 110 of them had CTE.
Because of this research, a growing number of elite-level football players are trying to get kids to wait until high school to start playing tackle. By then, kids’ bodies are developed enough that head trauma may not be as detrimental, and the kids can better understand proper tackling procedures and control their body to follow them.
Even if kids wait until they’re in high school to play tackle football, though, they’ll need something else to do in the meantime. And that’s where Sam Taggard’s kids have an advantage over Shantavia Jackson’s. Throughout the country, affluent school districts offer more extracurricular activities than poorer districts, and upper-income parents can pay for more activities outside of school. On top of hockey, the Taggards’ oldest son, Jack, plays trombone in the band, volunteers to teach music to disabled kids, enjoys chess, and skis. Jack expects to go to college whether or not he excels at sports. Both his parents did, and his father has a master’s in business administration. Shantavia Jackson is still working on getting her GED.
As brain-damage fears have grown, upper-income boys have started decamping to sports such as golf or lacrosse, which are less available in poorer communities. The kids are influenced by adults who have their own biases about the safety of football. Just 37 percent of white respondents told researchers that they would encourage kids to play the sport, while 57 percent of black respondents said they would, according to a working paper by the sociologists Andrew Lindner of Skidmore College and Daniel Hawkins of the University of Nebraska.

Now getting white kids just to play flag football can be a tough sell. Jim Schwantz, the mayor of Palatine, Illinois, and a former linebacker for the Dallas Cowboys and San Francisco 49ers, tried to start a flag-football league as an alternative for families in his area worried about concussions. Despite a strong start in 2012, interest fell each year in the mostly white suburbs where the league operated, because parents saw the sport as a gateway to tackle football. Schwantz decided to scrap the league in 2017.
Meanwhile, in Colquitt County, where the Jacksons live, football remains the biggest thing around. The county’s population is just 45,000, but it’s not unusual for the 10,000-seat high-school stadium to be full of local fans for Friday-night games. Timmy Barnes, a former player who later traveled with the football team as a police officer, has called Colquitt County “a community who only has football.” He wrote that after Rush Propst, the high-school coach, was nearly suspended after head-butting a player but was saved when he apologized and the community rallied around him.
On a fall afternoon, I sat with Shantavia Jackson on the metal bleachers of a high-school stadium in Thomasville, Georgia, a town in a neighboring county near the Florida border, as successive teams of boys came to play in a tournament branded “The Battle of the Babies.” Jackson was there from the start. She wore a gray long-sleeved Colquitt County Cowboys T-shirt to support her youngest son, Chance, whose Pop Warner team played in an early game. She cheered for him while keeping her 12-year-old, Jyqwayvin, entertained in the stands. Qway’s undefeated team was playing a team from Atlanta in the last game of the day, so the family’s day was dominated by football.
The stands were mostly empty when the 6- and 7-year-olds played around noon under a scorching Georgia sun, but they began to fill up as games featured older boys, who could run, jump, and hit harder than the little kids. Amid the sounds of the tournament—the cowbells and hollering from the parents, a DJ blasting Drake from the end zone, the referee’s whistles and the grunts of adolescent boys counting jumping jacks behind the stands—no one seemed bothered by the thuds of the hits. These happened constantly: when the 6- and 7-year-olds ran smack into one another trying to get a fumbled football, when a 9-year-old caught a pass and got leveled by a boy twice his size, and when an 11-year-old got yanked around the neck and tackled by another 11-year-old.
“Get him, come on!” a grandmother yelled at her grandson, a tiny 61-pound 9-year-old named Zain who was flattened by a boy 40 pounds heavier. Zain came off the field crying and his mother went to stroke his head. With the exception of Zain and his family, nearly every other player and family in the stands was black.
By the time Qway’s game rolled around, the stands were packed and the sun had set, turning the sky a purplish blue. The game was a rout; the team from Atlanta was faster, bigger, and more organized than Qway’s team, and so the boys started getting violent in frustration, tackling one another after the whistle, grabbing at necks to pull one another down. Parents yelled at the referees for what they perceived as missed penalties, and then turned on one another. “We’re in the sticks now!” one Atlanta parent yelled, taunting. Qway got hit in the groin, and Jackson stood at the bottom of the bleachers, her hand by her mouth, waiting to make sure he was okay.
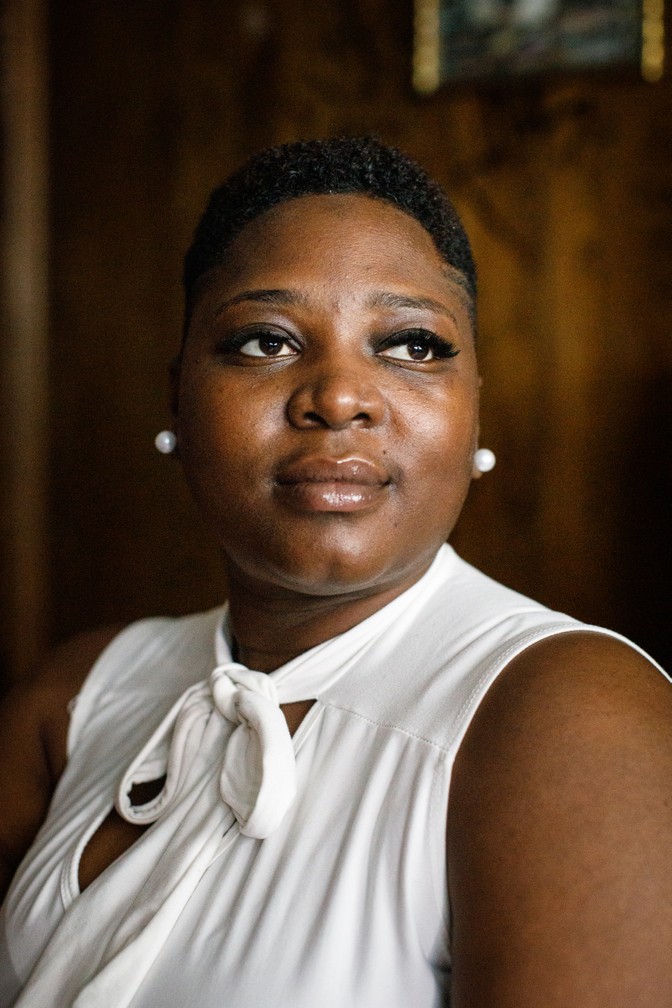

Jackson knows football is dangerous. Her father broke his neck playing football when he was in high school; he was in the hospital for weeks and had to get screws in his spine. But she has a fatalistic attitude about injuries. Her boys could get injured in a car accident or a drive-by shooting. They could get injured if they joined gangs. “If it’s meant to happen, it’s going to happen. We can’t stop it,” she said. “You can get injured in any sport.” All she can do, she told me, is hug her boys and tell them she loves them before each game.
Other parents in the stands said similar things. One mother: “Boys will be boys. They need a little roughness.” Another: “You have to keep your child busy so they don’t have time to get in trouble.” One woman, Hope Moore, started her son in football when he was 6. At first he wasn’t interested in playing sports, Moore said, but she wanted to get him off the couch and away from video games. He fell in love with football from the moment he started playing. Moore used to worry about the hits, pulling him from games if she thought he was getting hurt. But the coaches told her that her son needed to learn to make mistakes, and how to get hit, she told me. Now he’s getting invited to live in other school districts so he can be on their teams. “It’s going to help him in college,” Moore said.
Even as the dangers associated with tackle football become more evident, the sport is growing more lucrative. Universities can make money from football on ticket revenue, broadcasting fees, licensing opportunities, and sponsorships through bowl games. Some of the biggest schools have doubled what they make from football over the past decade, according to Forbes. The football program at Texas A&M University, one of the nation’s top teams, brings in $148 million annually.
Seeing the revenue opportunities, many schools have expanded their football program and started offering more scholarships. Since 1988, the NCAA has added 62 Division I schools that are eligible to offer full-ride football scholarships, representing about 3,000 more scholarships available. By contrast, 31 fewer schools offer NCAA Division I scholarships for men’s swimming and diving than in 1988. “If [universities] started giving boys the same amount of scholarships in swimming, you’d see a whole bunch of poor kids jumping in the pool,” Robert W. Turner II, a professor at George Washington University who briefly played in the NFL, told me.
In communities like Colquitt County, many families see high-school seniors get full-ride football scholarships and aspire to something similar. Jackson’s boys, for instance, look up to Ty Lee, a former Colquitt County football player who was recruited to Middle Tennessee State University. They visit him when he’s home from school. Around 78 percent of black male athletes in the lowest income quintile expect to qualify for financial aid through an athletic scholarship, compared with 45 percent of white males in the same income bracket, according to a forthcoming paper by the Portland State University sociologists CJ Appleton and Dara Shifrer.
College recruiting can happen as early as middle school, which means kids can feel pressure to start playing sooner to hone their skills. If parents in Colquitt County were to prevent their kids from playing until they’re 14, their kids’ athleticism and knowledge of the game would be far behind that of boys who have been playing for years. Chad Mascoe Sr., who played football at the University of Central Florida and in the Arena Football League, and who now lives in Thomasville, Georgia, told me that his 14-year-old son, Chad Mascoe Jr., had three recruiting offers before he got into high school. Now, as a star freshman, Chad has 13 offers, according to his father. He was recently recruited to transfer to an elite boarding and sports-training school in Florida later this year.
The NFL starts marketing to children when they’re young, which has attracted criticism from groups who say the league’s material portrays football as safe and healthy, even as research shows that it is not. The league runs a website and an app for kids that has 3 million registered users, and it has funded NFL-branded fitness and healthy-eating programs in more than 73,000 schools. A study published in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine found that the short-term health of students improved more in participating schools than in those not enrolled. In Colquitt County, schools got a visit from an Atlanta Falcons player through one of those programs in 2014. (The NFL declined to comment for this story.)
Even without the NFL’s presence, though, Colquitt County prioritizes football. In 2016, Colquitt County voters approved a ballot question that allowed the school board to use some proceeds of a sales tax for education funding to build a $3.7 million, 73,000-square-foot indoor multipurpose space that allows the football team to practice even in the heat of a Georgia summer. Propst, the high-school coach, made $141,000 last year, according to Open Georgia, which provides salary information for state and local employees. Most teachers at Colquitt County High School make less than half of what Propst does.

Without football, the options for boys in Colquitt County are limited. Only 80 percent of incoming freshmen at Colquitt County high schools end up graduating. Of those who do, just 29 percent go on to four-year colleges. For those who stay, job options are bleak: More than two-thirds of households in Colquitt County make less than $50,000 a year. That’s less than half the median household income in Connecticut’s Hartford County, where the Taggards live.
The people who do seem to be pulling their kids from football in Colquitt County are the ones who can afford other opportunities. I talked to Todd Taylor, who is white and lives in Moultrie, Georgia, a few miles from Shantavia Jackson’s hometown of Norman Park. He played football and baseball at Colquitt County High, and his family has season tickets to Colquitt County Packers football games. But his wife really doesn’t want their 8-year-old son, Jud, to play, because of concussion dangers. Instead, Jud plays baseball and dives at Moss Farms Diving, a powerhouse facility in Moultrie that has trained dozens of divers who get college scholarships. Moss Farms offers training tuition-free to those who need it, but diving remains an expensive sport in America, requiring pool time and lots of travel. Sixteen percent of the Moss Farms roster is made up of people of color.
The divide on the football field makes it hard not to see how inequality in America is worsening health disparities and raising the specter of another, darker era of American history. In the early part of the 20th century, black Americans were prevented from buying homes in well-off neighborhoods by racially restrictive covenants, excluded from trade unions and the jobs they guaranteed, and paid less than their white counterparts. The segregation that resulted has long had health implications. Today simply the fact of being black can be hazardous to one’s health. Low-income black boys are more likely than low-income white boys to live in neighborhoods with persistent poverty, violence, and trauma. These neighborhoods also have little access to healthy foods.
Despite the benefits football can provide, it may also be worsening these health disparities. The medical care accessible to low-income families in poor neighborhoods may be helping to obscure the dangers of brain injuries. Low-income black communities have less access to good medical services and information that would emphasize the downsides of playing football, says Harry Edwards, a civil-rights activist and emeritus professor of sociology at the University of California at Berkeley. “Nobody advises them as to the long-term medical risks,” he told me. “They are out of the loop.” Black people who said they had followed news about concussions were less likely to encourage children to play football than others who hadn’t been following the news, according to Lindner and Hawkins’s study.
When black boys from low-income families look for examples of men who have come from similar backgrounds and succeeded, they don’t have as many positive role models outside of sports and music. Black NFL players who came from poverty are featured in commercials selling products, sitting behind desks at halftime in tailored suits, holding up trophies. They’re in newspaper stories and TV specials in which they talk about growing up poor in the South, raised by a single mother, and making it big in the NFL. “The media serves up encouraging stories for black kids to consume,” says John Hoberman, the author of Darwin’s Athletes: How Sport Has Damaged Black America and Preserved the Myth of Race. Low-income black boys do not see the hundreds of athletes suffering in silence as their brain deteriorates, who ache when they get out of bed every morning, who damaged their body playing in high school or college but who didn’t even make it to the NFL.
While black boys are disproportionately getting channeled into a violent sport, white people are making the most money off of it. Seventy percent of NFL players are black, but only 9.9 percent of managers in the league office are. The NFL was just 52 percent black in 1985. Only two people of color are majority owners of NFL franchises: Shahid Khan, the Pakistani American owner of the Jacksonville Jaguars, and Kim Pegula, a Korean American businesswoman who is a partial owner of the Buffalo Bills. “If you’re going to avoid 21st-century gladiator circumstances in terms of football, the teams have to look something like the demographic representation of this nation,” Edwards told me.
Last year, the NFL expanded its Rooney Rule, which was first implemented in 2003 and seeks to diversify teams’ coaching and front-office staff. Still, the gladiatorial overtones are hard to overlook. Players who want to get recruited by NFL teams must attend the NFL Scouting Combine, a week-long showcase in which they perform mental and physical tests. Athletes’ hand size, arm length, and wingspan are measured during this event, and players are asked to stand naked but for their workout shorts so that team recruiters can see how they are built, according to Edwards, who also works as a consultant with the San Francisco 49ers. NFL and team executives, mostly white men, are evaluating the bodies of black players, deciding whether to make an investment.
Even as broadcast networks lost viewers generally, NFL ratings were up in 2018. Americans still appear to have a growing fascination with the sport, even if a majority-white segment of the population doesn’t want their children to play it.
Without a reversal in economic fortunes for poor communities across the country, football could one day become a sport played almost exclusively by black athletes, while still enjoyed by everyone. Black athletes—who already make up the majority of players in the most dangerous on-field positions—would continue to suffer from long-term brain damage, their life cut short by dementia and the scourge of CTE. Black boys would continue to be drawn to a sport that could make their life painful and short. Everyone else would sit back and watch.
Efforts are under way to try to make football safer. Youth leagues are implementing concussion protocols, lessening the amount of hitting players do in practice, and even distributing helmets with special sensors that analyze whether an athlete has gotten a concussion. Dartmouth College eliminated live tackling in all practices in 2010; other Ivy League schools adopted similar rules in 2016. The NFL has made some changes, too, adding a concussion protocol in 2009 and altering kickoff and tackling rules to lower the risk of injury. The 2018 NFL season saw a 28 percent decrease in concussions, compared with the previous year.
Still, the league can’t do much about the fact that football, more than any other sport, requires players to run into one another over and over again and fall to the ground. “Football at the elite level is about as close as you can get to war and still stay civil,” Edwards said. Concussion protocols can’t erase the research that suggests that primarily brain trauma, not concussions, leads to CTE.

Some lawmakers want the government to get involved by prohibiting kids from tackling in football before high school, or by banning youth tackle football entirely. Bills introduced in five states to restrict tackle football have faced backlash. “To demonize just this sport is unfair. It’s illogical, and frankly, it’s downright un-American,” Mike Wagner, the executive commissioner of Pop Warner’s Southern California conference, said in reaction to the Safe Youth Football Act, a failed California bill introduced last year that would have set a minimum age for organized tackle-football leagues.
The disappearance of tackle football could be a real blow to some communities, unless something changes so that those places offer more opportunity and less peril for low-income black boys. If tackle football were banned, for instance, Shantavia Jackson’s boys would lose the coaches who look out for them. Without football, they wouldn’t have something to look forward to on weekends, or as big of a community of teammates. They might not have a dream they can pursue that’s quite as tangible and achievable as playing college football.
Before she had kids, Jackson wanted to leave Colquitt County, but she ended up staying in the same town where her father and grandmother still live. The stakes are higher for her sons, she says, especially for Qway, whose mental-health condition sometimes sets him apart. He needs to be somewhere bigger, with more people like him, she told me. “There’s really nothing much here for him,” she said.
White parents may be doing the best thing for their sons by pulling them from tackle football. But parents of black boys in the rural South are facing a different reality, Jackson says. She believes that she is being a good parent if she gets her sons excited about tackle football. Their opportunities grow if they learn how to hit and tackle and run—how to be as much of a live wire—as well as they possibly can.
* This article previously misstated the university Sam Taggard attended.